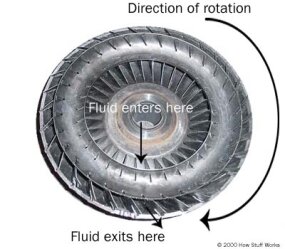
In short the torque converter is filled with transmission fluid and has a fan or turbine-like unit inside. When the engine runs it rotates the impeller and due to the centrifugal force the oil inside the torque converter assembly directed towards the turbine.

The impeller is a piece with tilted blades that look somewhat like a fan.
Inside of a torque converter. On this PowerNation Extra the Engine Power team goes over whats inside a torque converter how it works and explains how its not magic that determines th. Whats Inside a Torque Converter. The impeller sometimes known as a pump is attached to and spins with the engines crankshaft.
When the fluid hits the turbines blades the turbine spins and funnels the fluid to the center of the turbine. Torque cannot be. The whirlpool action inside the torque converter is controlled by the stator.
The stator sits on a one-way clutch in between the two rotating vanes. The extreme angled fins redirect the fluid from the turbine before it returns to the impeller. This action improves performance and fuel efficiency greatly.
The major components of a torque converter are the impeller the turbine and the stator. Theres also the fluid itself and often a lock-up clutch. All are contained within the housing of the torque converter which connects to the engines flexplate sometimes called the flywheel.
Impeller - The component that is connected to the engine. As shown in the figure below there are four components inside the very strong housing of the torque converter. Pump Turbine Stator Transmission fluid.
Inside the torque converter are three main parts. The first part of the assembly is called the impeller also known as the pump. It is filled with fluid and it spins with the engine crankshaft.
The faster it spins the more force is created as the fluid flows through it faster and harder. A torque converter is a type of fluid coupling which transfers rotating power from a prime mover like an internal combustion engine to a rotating driven load. In a vehicle with an automatic transmission the torque converter connects the power source to the load.
It is usually located between the engines flexplate and the transmission. The equivalent location in a manual transmission would be the mechanical clutch. The main characteristic of a torque converter is its ability to increase torqu.
It is however a very impo. In short the torque converter is filled with transmission fluid and has a fan or turbine-like unit inside. The more it rotates the more pressure it creates inside the unit and the more power is transferred from the engine to the transmission.
If you cut open a race torque converter inside you will find. The turbine stator with sprag and impeller pump. The converters turbine is attached to the drivetrain via the input shaft of the transmission.
When the turbine moves the car moves. The stator is the fluid director and changes fluid flow between the turbine and pump. Torque converters are comprised of five main components.
The impeller the turbine the stator a clutch and the fluid. The stator is what makes a torque converter a torque converter. Without the stator its just the fluid coupling.
The impeller is a piece with tilted blades that look somewhat like a fan. In that the impeller or pump acts as first fan which is connected to the engine and turbine act as the second fan which is connected to the transmission system. When the engine runs it rotates the impeller and due to the centrifugal force the oil inside the torque converter assembly directed towards the turbine.
Other changes made inside the F3 converter include the use of a Torrington thrust bearing for increased strength over factory plastic bearings. The torque converters front cover is also upgraded to a custom-machined billet cover that helps eliminate ballooning of the cover under extreme heat and in high-torque situations. The torque converter is a fluid coupling for automatic transmissions that allows the engine to transfer power to the transmission.
When accelerating the torque converter transfers increased torque to the transmission. When in neutral park or slowing to a stop the torque converter isolates the engine rotation from the transmission. Your torque converter is essentially a hydraulic pump that acts as the link between the engine and the transmission.
Various components within the torque converter use vanes similar to a turbine to act on the transmission fluid within the unit to create a fluid coupling as well as provide the fluid pressure that the transmission needs. The pump of the torque converter is made up of small fins that make the connection to the flywheel possible. They also serve to pump the transmission fluids to the outside of the mechanism.
This creates a vacuum that in turn delivers more fluid to the central part of the device. Torque converters can be serviced or replaced as a single unit. There are many different types of torque converter problems.
The problems come in many sizes shapes and forms. But the most common torque converter problems are listed below.