Viscosity refers to a fluids resistance to flow. An oil is rated for viscosity by heating it to a specified temperature and then allowing it to flow out of a specifically sized hole.

The viscosity of an oil is measured by its resistance to flow.
What is engine oil viscosity. The term viscosity refers to the thickness of the oil and its resistance to flow. A higher oil viscosity number indicates a thicker oil. Where this is vitally important is in an engines bearing clearances.
The main requirements for an engine oil are defined temperature-viscosity properties protection against wear and corrosion keeping the engine clean holding particles like soot or abrasives in suspension yield strength under compression and many more. Temperature impacts the flow properties of engine oil. Engine oil is available in different.
Oil viscosity is the parameter that plays an important role in lubrication. It changes with temperature shear rate pressure and thickness. Oil viscosity is graded by measuring the time it takes for a standard amount of oil to flow.
Motor oil viscosity is a common term we need to understand completely and it refers to the ability of an oil to flow. Motor oil viscosity is generally known as a measurement of thickness. But more specifically viscosity determines an oils resistance to flowing in liquid form as well as its resistance to shearing breaking down as its slammed around inside an engine.
Viscosity is the most important property of oil when considering engine protection. Viscosity determines how your engines lubricant will react to changes in speed pressure and temperature. For example during cold winter months it may be difficult to get your car to start first thing in the morning.
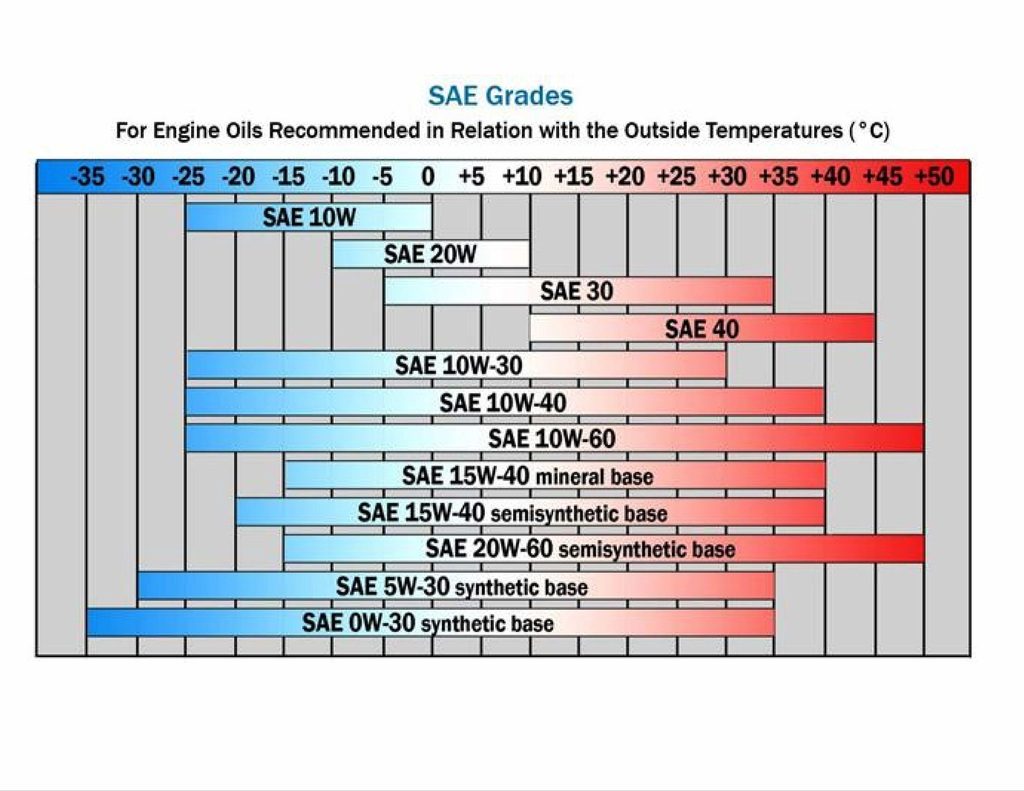
When it comes to automotive engine lubrication we often prefer oils with a low viscosity spectrum but a High Viscosity Index– in short this means that the viscosity stays static over a wider range of temperatures. This occurs via unique additives referred to as Viscosity Index Improvers VI improvers. When you see an oil thats rated SAE 30 this translates into an engine oil that has a viscosity between 93 cSt and 125 cSt at 212 degrees F.
Multigrade Oils Sometimes it gets much colder than room temperature particularly during the winter months when the thermometer can plunge well below freezing. When you see a W on a viscosity rating it means that this oil viscosity has been tested at a Colder temperature. The numbers without the W are all tested at 210 F or 100 C which is considered an approximation of engine operating temperature.
In other words a SAE 30 motor oil is the same viscosity as a 10w-30 or 5W-30 at 210 100 C. The difference is when the viscosity is tested at a much colder temperature. The w in motor oil stands for winter.
The first number in the oil classification refers to a cold weather viscosity. The lower this number is the less viscous your oil will be at low temperatures. For example a 5W- motor oil will flow better at lower temperatures than a 15W- motor oil.
Viscosity by definition is an oils resistance to flow and shear. It is the single most critical physical property of the oil as it affects both the wear rate and the fuel efficiency. Water is a low viscosity fluid.
Syrup is a high viscosity fluid. Motor oil engine oil or engine lubricant is any one of various substances that consist of base oils enhanced with various additives particularly antiwear additives detergents dispersants and for multi-grade oils viscosity index improversMotor oil is used for lubrication of internal combustion enginesThe main function of motor oil is to reduce friction and wear on moving parts and to. Viscosity is affected by three things temperature pressure and the speed that you shear it which relates to engine speed.
Mostly we are working at atmospheric pressure or a bit above so we can consider that relatively constant. The viscosity of an oil is measured by its resistance to flow. There are two numbers that define the viscosity of an oil.
The first number ends with the letter W which stands for Winter. This measurement is related to how an oil flows when it is cold such as at engine start-up. When comparing engine oils for your ride the most important thing to keep in mind is the oils viscosity rating.
Look for the viscosity grades recommended by the original equipment manufacturer OEM which you can locate in your owners manual. Viscosity refers to a fluids resistance to flow. Most motor oils viscosity is rated based on how thick it is at zero degrees Fahrenheit represented by the number preceding the W which stands.
An oil is rated for viscosity by heating it to a specified temperature and then allowing it to flow out of a specifically sized hole. Its viscosity rating is determined by the length of time it takes to flow out of the hole. If it flows quickly it gets a low rating.
If it flows slowly it gets a high rating. Engine oil viscosity refers to how easily oil pours at a specified temperature. Thin oils have lower viscosity and pour more easily at low temperatures than thicker oils that have a higher viscosity.
Thin oils reduce friction in engines and help engines start quickly during cold weather. Choosing the correct oil viscosity can be an important factor in determining the life expectancy and performance of your engine. Using the correct-viscosity oil can also keep the engine running at its peak efficiency and plays a small part in the overall fuel economy of your vehicle.